“`html
Cybercriminals have advanced their social manipulation strategies with a complex malware initiative that takes advantage of users’ confidence in financial institutions.
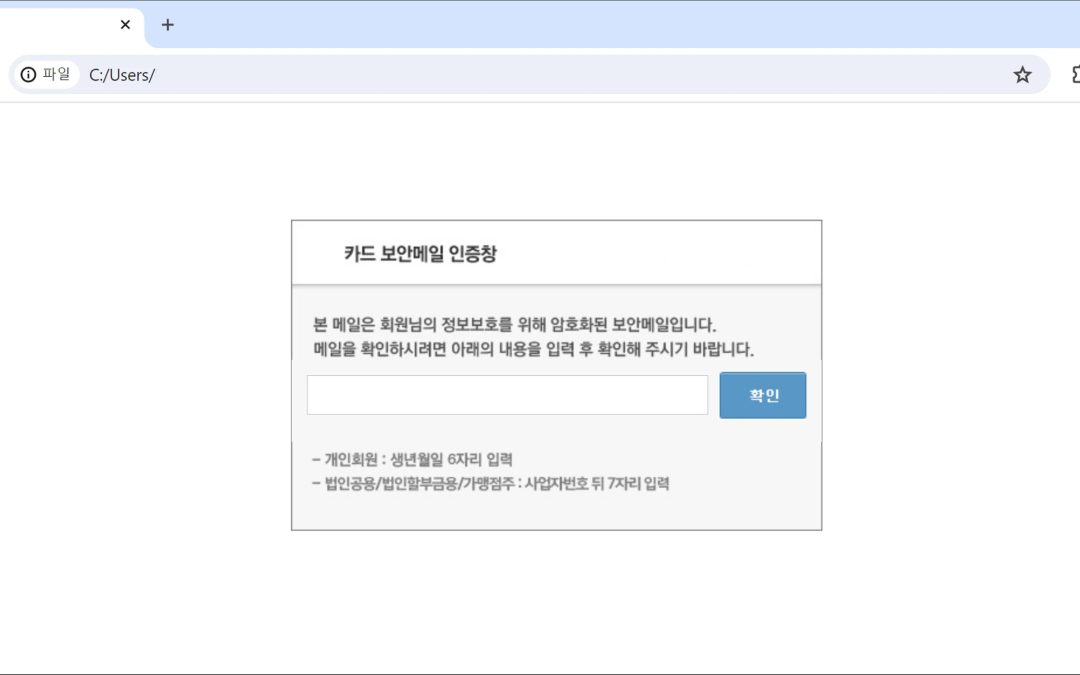
The newest menace entails a malicious LNK file posing as a credit card security email verification popup, specifically aimed at naive users through misleading filename patterns like card_detail_20250610.html.lnk.
This assault signifies a troubling evolution in malware dissemination techniques, utilizing the urgency and authenticity linked to credit card security alerts to evade user doubt.
The initiative showcases sophisticated evasion strategies by integrating genuine decoy files alongside harmful payloads.
In contrast to conventional assaults that hinge on document-based decoys, this threat actor utilizes HTML files to fabricate convincing authentication pages for credit card firms.
When users activate the LNK file, the malware concurrently downloads and presents a convincing HTML page, effectively concealing its malicious actions while preserving the facade of a legitimate security procedure.
ASEC analysts discovered this emerging threat through their ongoing surveillance of malware distribution initiatives.
The researchers observed that threat actors have greatly refined their impersonation strategies, particularly targeting esteemed financial entities to enhance their success rates.
This trend illustrates how cybercriminals increasingly leverage institutional trust to facilitate initial breaches.
Advanced Infection and Persistence Mechanism
The malware’s infection chain reveals intricate multi-phase deployment abilities.
Upon activation, the LNK file initiates the download of an HTA file and the decoy HTML document into the system’s temporary folder.
The HTA component subsequently generates two vital files in the C:Users{username}AppDataLocal directory: sys.dll (the primary malicious payload) and user.txt (containing download links for supplementary components).
.webp)
The malware utilizes the Reflective DLL Loading method via rundll32.exe, allowing it to run three specialized modules: app, net, and notepad.log.
The app module specifically targets Chromium-based browsers including Chrome, Brave, and Edge for credential theft, while net broadens the focus to include Opera, Firefox, and significant web services like Google, Yahoo, Facebook, and Outlook.
The notepad.log component serves as a comprehensive backdoor, offering remote shell access, file enumeration capabilities, and keylogging functions that store captured information in the C:Users{username}AppDataLocalnetkey directory.
The post Weaponized LNK File Disguised as Credit Card Security Email Steals User Data appeared first on Cyber Security News.
“`